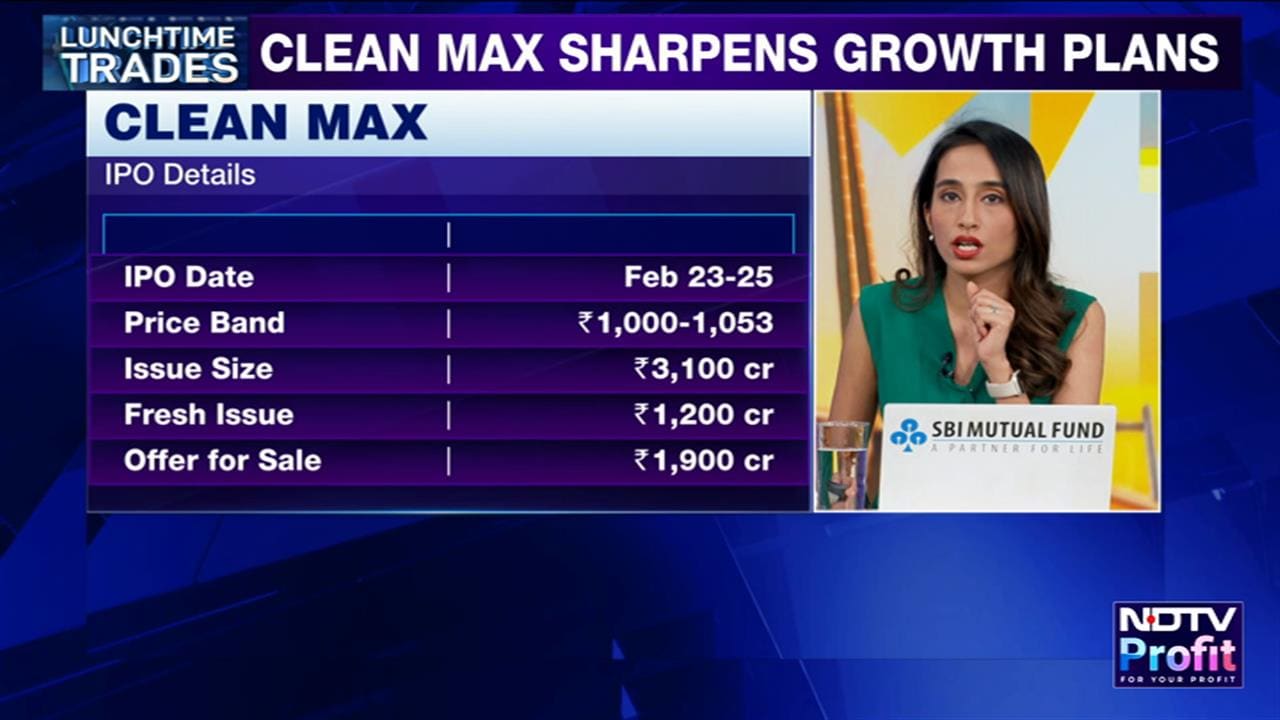NASA on Monday announced that its Deep Space Optical Communications experiment beamed an ultra-high definition streaming video on Dec. 11 from a record-setting 19 million miles away (31 million kilometers, or about 80 times the Earth-Moon distance).
The milestone is part of a NASA technology demonstration aimed at streaming very high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space – enabling future human missions beyond Earth orbit, the space agency said in a statement.
The 15-second test video featuring Taters, a tabby cat was transmitted via a cutting-edge instrument called a flight laser transceiver.
We just streamed the first ultra-HD video brought to you via laser from deep space. And it's a video of Taters, a tabby cat.
December 19, 2023
This test will pave the way for high-data-rate communications in support of the next giant leap: sending humans to Mars. https://t.co/tf2hWxaHWO pic.twitter.com/c1FwybYsxA“This accomplishment underscores our commitment to advancing optical communications as a key element to meeting our future data transmission needs,” said NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy.
“Increasing our bandwidth is essential to achieving our future exploration and science goals, and we look forward to the continued advancement of this technology and the transformation of how we communicate during future interplanetary missions.”
The video signal took 101 seconds to reach Earth, sent at the system's maximum bit rate of 267 megabits per second (Mbps).
Capable of sending and receiving near-infrared signals, the instrument beamed an encoded near-infrared laser to the Hale Telescope at Caltech's Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, where it was downloaded.
Each frame from the looping video was then sent “live” to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, where the video was played in real time, NASA said.
According to NASA, the laser communications demo, which was launched with Psyche mission on Oct. 13, is designed to transmit data from deep space at rates 10 to 100 times greater than the state-of-the-art radio frequency systems used by deep space missions today.
Who Is Taters?
Uploaded before launch, the short ultra-high definition video features an orange tabby cat named Taters, the pet of a JPL employee, chasing a laser pointer, with overlayed graphics.
The graphics illustrate several features from the tech demo, such as Psyche's orbital path, Palomar's telescope dome, and technical information about the laser and its data bit rate. Tater's heart rate, colour, and breed are also on display.
“Despite transmitting from millions of miles away, it was able to send the video faster than most broadband internet connections,” said Ryan Rogalin, the project's receiver electronics lead at JPL.
“In fact, after receiving the video at Palomar, it was sent to JPL over the internet, and that connection was slower than the signal coming from deep space. JPL's DesignLab did an amazing job helping us showcase this technology – everyone loves Taters,” he said.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.