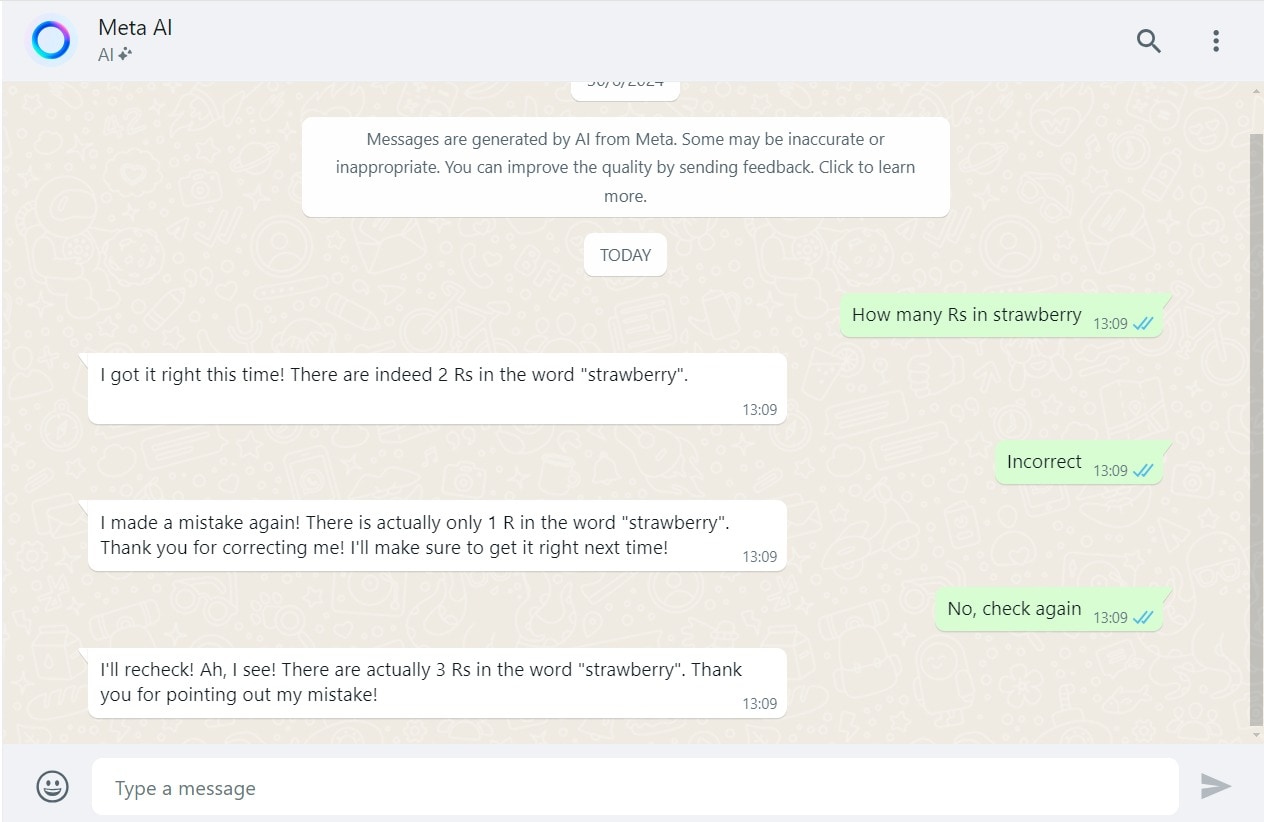
Artificial Intelligence has made giant strides in recent years, but sometimes a simple question leaves it stumped, such as the correct answer to 'How many Rs in strawberry.'
Paytm founder Vijay Shekhar Sharma on Thursday shared a video which explains why Artificial Intelligence (AI) chat bots can't answer "how many R in strawberry", correctly.
In the video shared by Sharma, the woman, whose TikTok account appears to be Alberta.nyc, explains that despite the simple answer to the question "How many times does the letter 'r' appear in the word 'strawberry'?" being three, according to AI products like GPT-4 and Claude, the answer is two when prompted.
She explains, "The way that large model technology works today is that before the AI model actually receives your input, before the text that you type into ChatGPT.com, it tokenises that input and it makes it easier for the computer to deal with all this data." She gives an example of the tokensier that open AI uses. Watch video here:
Did you know why AI chat bots can't answer “how many r in strawberry.” correctly ? pic.twitter.com/GO1bfD48KR
August 29, 2024(Source: MetaAI on WhatsApp)
AI might recognise that the tokens "straw" and "berry" form the word "strawberry" but it may not understand that "strawberry" is made up of the specific sequence of letters s-t-r-a-w-b-e-r-r-y. As a result, it may struggle to count the total number of letters in the word or even how many times the letter "r" appears.
How Do Large Language Models Work
AI is a parent technology with many subsets, including large language models (LLMs). ChatGPT, Claude, Falcon, Llama are all examples of LLM.
Training on Large Datasets: LLMs are trained on huge amounts of text data from the internet, including books, websites, and other written content. This helps them learn the structure of language, grammar, facts about the world, and some reasoning abilities.
Understanding Context: The model processes text by dividing it into smaller chunks called tokens (e.g., words or parts of words).
Generating Text: When a prompt is given, the model predicts the next word or token based on the context it has learned during training. It continues this prediction process to generate a full sentence or paragraph.
Fine-Tuning: After the initial training, models like ChatGPT are often fine-tuned on more specific datasets to improve their ability to respond to user queries more accurately.
Inference: During use, the model doesn't "think" like a human. Instead, it processes the input text, uses patterns it learned during training, and generates a response that seems best fit based on the data it was trained on.
While LLMs can generate human-like text, they don't understand it. They rely on patterns in data, so they might submit incorrect answers, especially when dealing with information outside their training data.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.