(Bloomberg) -- As Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi bids for reelection, his party has said his skillful diplomacy on the world stage has increased India's global stature and brought in a flood of investment.
But what exactly have Modi's foreign travels achieved? With 92 trips to 57 countries since coming to power in May 2014, Modi has flown abroad nearly twice as much as his predecessor Manmohan Singh in five years.
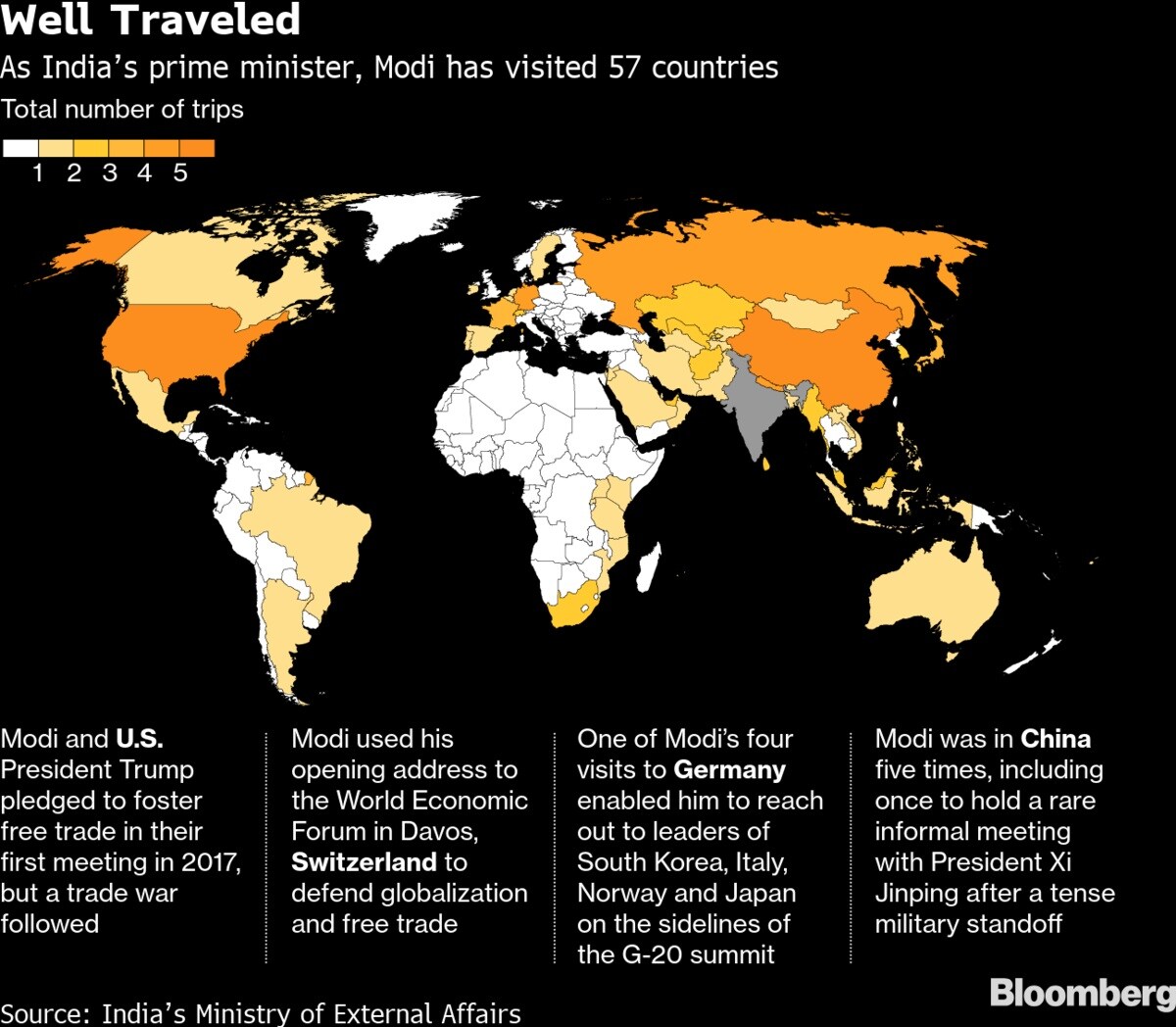
While Modi's visits have won praise from supporters for boosting India's global profile, the costs associated with them -- and the optics of traveling abroad so often in a country where many farmers are struggling -- have triggered some criticism. The main opposition Indian National Congress leader Rahul Gandhi has accused Modi of ignoring problems at home.
A closer look at Modi's trips show that while some have yielded vague agreements that may not develop into anything substantial, doubters may still be exaggerating the negatives. Summit meetings accounted for roughly a third of Modi's visits. And his arrival in each foreign capital made a symbolic statement about New Delhi's world outlook.
Modi also made a point of repeatedly meeting leaders such as Japan's Shinzo Abe and Russia's Vladimir Putin, whose countries provide much-needed industrial investment and defense technology. Here's more:
Record FDI
Foreign direct investment into India in Modi's first term amounted to $193 billion, 50 percent more than the preceding five years.
At the same time, despite a high-profile push to generate jobs through manufacturing, much of the FDI has continued to flow into India's services and capital-intensive industries, not labor-intensive ones.
While Modi won investment commitments from longstanding economic and strategic rival China, it largely remains a non-starter. FDI from China totaled $1.5 billion in the four years to March 2018, data from India's central bank show, against $20 billion President Xi Jinping promised in the five years from 2014.
Energy Security
Under Modi, India started purchasing crude and liquefied natural gas cargoes from the U.S. for the first time. In the last five years, he struck deals from Russia to the Middle East securing oil assets for India. He got the world's biggest oil exporter Saudi Aramco to agree to invest in India's largest oil refinery, and the U.A.E. to fill up strategic oil reserves, reducing the strain on state finances.
More broadly, Modi has maintained relations with Gulf countries crucial to India's energy security even as he strengthened ties with Iran. However, the opposition has criticized the prime minister's diplomacy for failing to win continued access to cheaper Iranian crude in the face of increasing U.S. pressure on Tehran.
Big Projects
Modi has tried to tap a number of countries for strategic projects, which has occasionally brought him political grief.
After making the first-ever visit to Israel by an Indian premier, Modi has continued to seek advanced defense and water technology from Tel Aviv. With Japan, India is building a bullet train in Modi's native Gujarat state -- although the slow pace of land acquisition has led to criticism.
In 2016, Modi signed an $8.7 billion deal for 36 Rafale fighter planes from France. The move has come under intense scrutiny since then for alleged rule violations, which his government has denied. Opponents have continued to use the deal to question the government's anti-corruption credentials.
Soft Power
Modi has tried to use his trips to bolster India's global image as an investment destination and a rising global power. He's addressed the World Economic Forum in Davos and the Shangri-La security dialogue in Singapore.
Modi used a rare informal summit with China's Xi in the city of Wuhan last year to patch up geopolitical tensions between New Delhi and Beijing following a military stand off in the Himalayas.
However several trips, including a surprise visit to Pakistan in 2015, did not yield any tangible results. And though Modi has approached diplomacy with vigor, some analysts suggest he has not injected the resources -- or implemented the reforms -- necessary to improve India's standing in the world.
--With assistance from Adrian Leung and Debjit Chakraborty.
To contact the reporters on this story: Karthikeyan Sundaram in New Delhi at kmeenakshisu@bloomberg.net;Iain Marlow in New Delhi at imarlow1@bloomberg.net;Hannah Dormido in Hong Kong at hdormido@bloomberg.net
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Ruth Pollard at rpollard2@bloomberg.net;Nasreen Seria at nseria@bloomberg.net
©2019 Bloomberg L.P.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























