
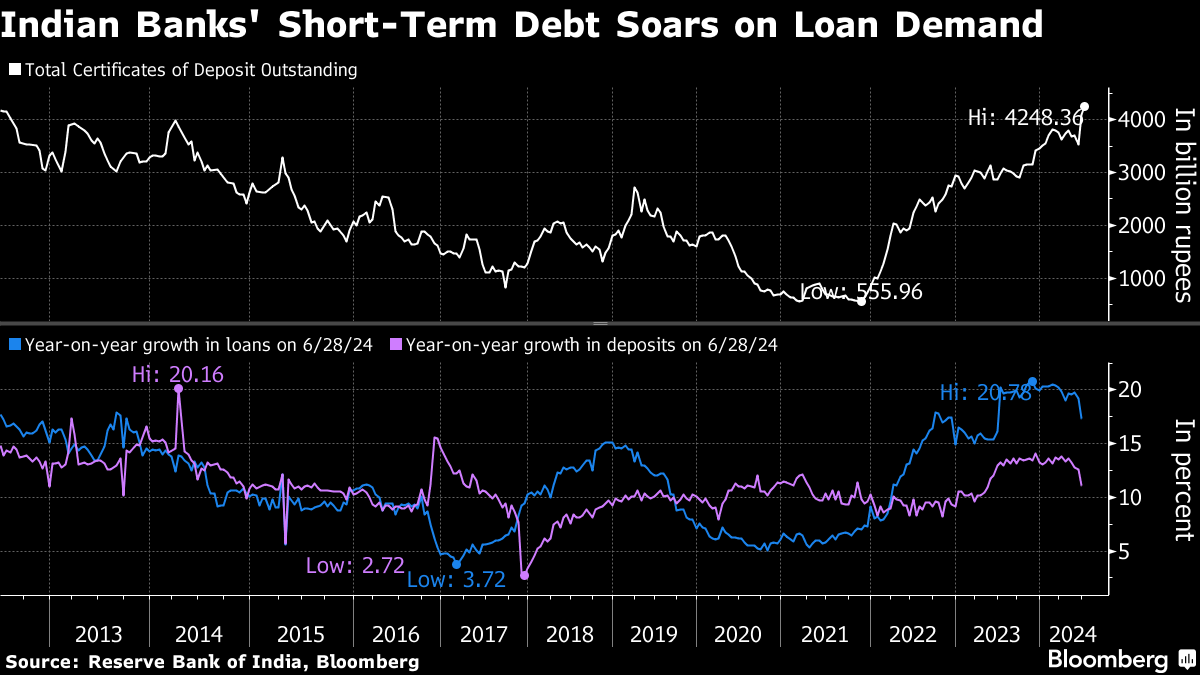
(Bloomberg) -- Indian banks are increasingly turning to shorter-maturity borrowing to bridge a funding shortfall caused by robust loan growth and dwindling deposits.
The outstanding amount of certificates of deposit issued by banks rose to 4.3 trillion rupees ($51.4 billion) in the fortnight through July 12, according to the latest data by the Reserve Bank of India. That's the highest since June 2012, and came as bank loans expanded at 17.4% in the year through June 28, higher than the 11% growth in deposits.
Reserve Bank of India Governor Shaktikanta Das last week warned that such borrowings increase lenders' sensitivity to interest-rate movements and pose challenges to liquidity management. Bank's deposit growth may be lagging as households shift their savings to financial markets, he added.
“Amid stiff competition, it has been tough to garner deposits even after the lenders have raised their deposit rates,” said Rena Kwok, credit analyst at Bloomberg Intelligence. “So they have to turn to other funding sources to meet the strong loan demand. In the near-term, deposit growth may still be a challenge.”
Depositors in India have been saving less in banks as soaring equity markets and avenues such as mutual funds, insurance funds and pension funds lure them.
To deal with the wide credit-deposit gap, some banks have raised term deposit rates, while HDFC Bank Ltd. is mulling the sale of a loan portfolio. Banks have also raised unprecedented amounts from the local-currency bond market to fund infrastructure and affordable housing projects.
Higher borrowing via certificates of deposits may hurt banks' net interest margins as this funding is costlier than term deposits, said Soumyajit Niyogi, director at India Ratings & Research Pvt., the local arm of Fitch Ratings.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























