
(Bloomberg) -- Years of harrowing losses have left Chinese stocks with a diminished standing in global portfolios, a trend that's likely to accelerate as some of the world's biggest funds distance themselves from the risk-ridden market.
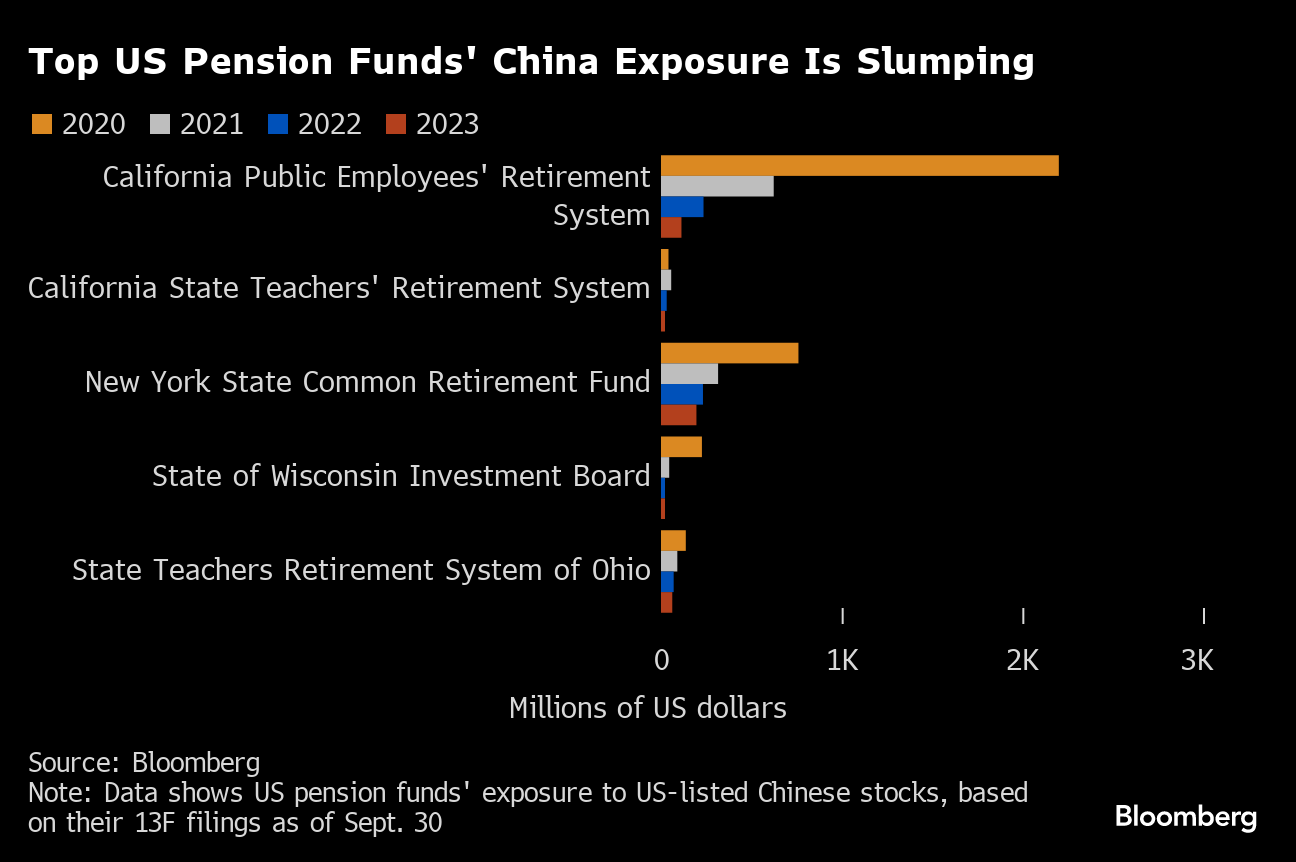
An analysis of filings by 14 US pension funds with investments in Chinese stocks show most of them have reduced their holdings since 2020. The California Public Employees' Retirement System and New York State Common Retirement Fund, among the nation's biggest pension investors, cut their exposure for a third straight year.
What started out as a performance-driven exodus now risks becoming a structural shift due to a toxic combination of doubts over Beijing's long-term economic agenda, a prolonged property crisis and strategic competition with the US. Money managers at some of the biggest pensions in the US and Australia said in interviews that the prevailing playbook for China is one of caution.
“Foreign investors no longer fear leaving China out of their investment universe,” said Gary Dugan, chief investment officer at Dalma Capital Management Ltd. “We sense that international investors are just giving up trying to read China and will revert to a world-ex-China opportunity set, hence resetting the benchmarks to MSCI World ex-China.”
Some are exiting entirely.
Missouri State Employees' Retirement System in December told its staff to “divest from all of its current global public equity investment in China.” That came a month after the Federal Retirement Thrift Investment Board said it will exclude investments in Hong Kong, in addition to mainland China, from its $68 billion international fund. It cited Washington's increasing investment restrictions on China as a key reason for the decision.
“China is a recurring discussion among US and global CIOs,” Chris Ailman, chief investor officer of the California State Teachers' Retirement System, said in an interview. “Some have cut their index weight in half to reduce their exposure and a few have dropped China from their emerging market index.” Calstrs's decision is to “not be overweight nor underweight but index weight,” he said.
His comments come as China's share in the MSCI Emerging Markets Index dropped to 23.77% as of end-December, the lowest since mainland stocks were added to the gauge in 2018. In the Asia Pacific Index, China now accounts for about 15%, down from 24% in 2020.
READ: China's Weight in Emerging-Market Index Drops to Record Low
A 2023 survey of 100 pension and sovereign wealth managers by London-based think-tank Official Monetary and Financial Institutions Forum found none of them have a positive outlook on China, or see higher relative returns.
It's a far cry from the late 2010s when the country's economic ascent and manufacturing prowess made overseas investors eager for a slice of the booming market. If MSCI's addition of A-shares showcased China's global acceptance, its falling status speaks to that allure fast fading.
Bloomberg analyzed 13F filings by 271 American pension funds with assets over $500 million. Among them, 14 had investments in US-listed Chinese stocks.
Underscoring how Chinese markets are dropping off radars, their low valuations aren't helping. The MSCI China Index has never been this cheap versus the S&P 500 when looking at forward earnings estimates, trading at a 56% discount. The estimated price-to-earnings ratio is below its five-year average.
Australia's second-largest pension fund, the A$260 billion ($174 billion) Australian Retirement Trust, is wary of raising its China holdings beyond what's needed to stay in line with performance benchmarks.
“In public equities, we are just trying to make sure that we have a benchmark exposure and we do it in a way that doesn't tie up liquidity unnecessarily,” said ART's Chief Investment Officer Ian Patrick. “It's a big economy where valuations are challenged and so there's definitely opportunity there.” He added the bigger question was how the global order plays out between China and the US, and other countries.
Read: China's Woes Spell Caution for Australia's Biggest Investors
As long-term investors shun China, the market risks becoming even more dominated by local traders — heightening volatility and scaring away global funds. The MSCI China Index has extended declines after capping a third annual loss. Money managers deem tensions with the US and Europe, the state's grip over the private sector, and the economy's downward trend as having permanently undermined its attraction.
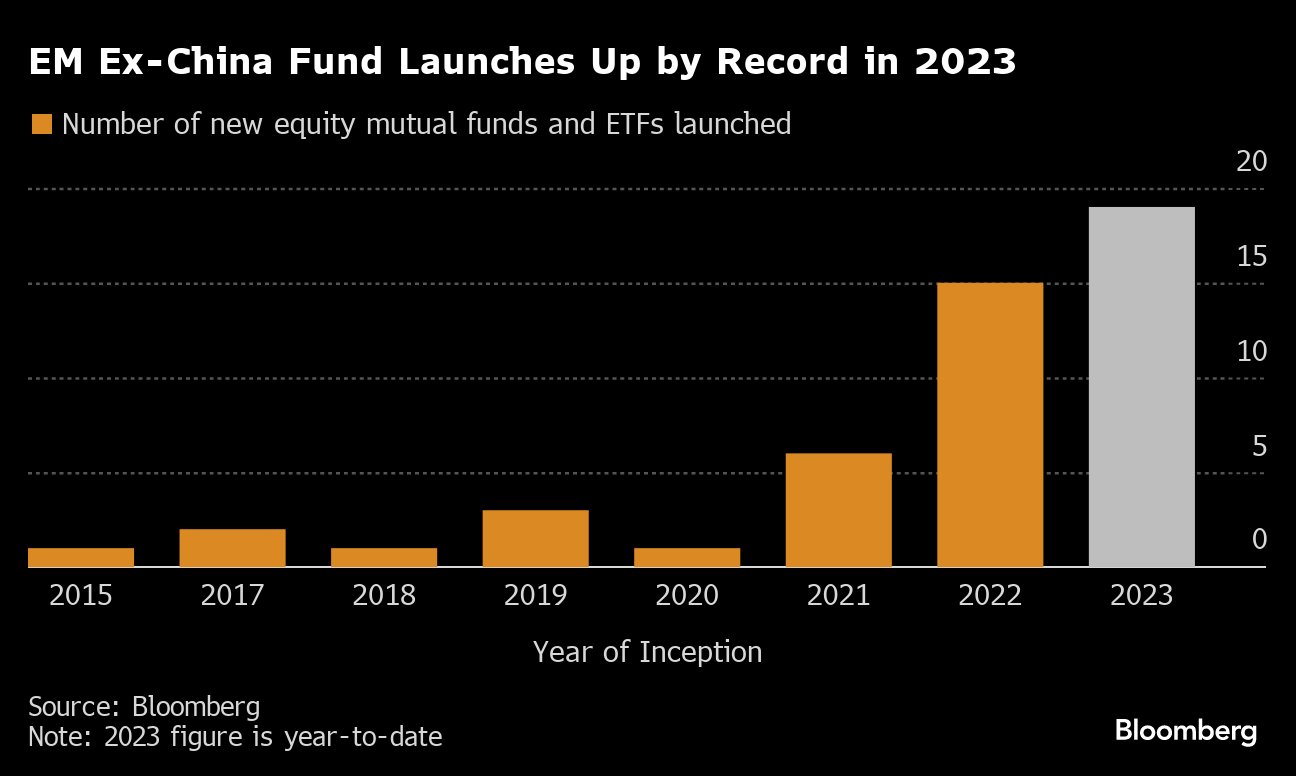
As China flops, investments excluding the country have prospered. The number of new EM equity-focused funds with no China exposure reached 19 in 2023, up from 15 in 2022 and just one in 2020, data compiled by Bloomberg show.
Wall Street titans including Goldman Sachs Asset Management and BlackRock Inc. have launched new EM ex-China funds earlier last year, while Robeco and Vontobel Holding AG have more recently joined the wave.
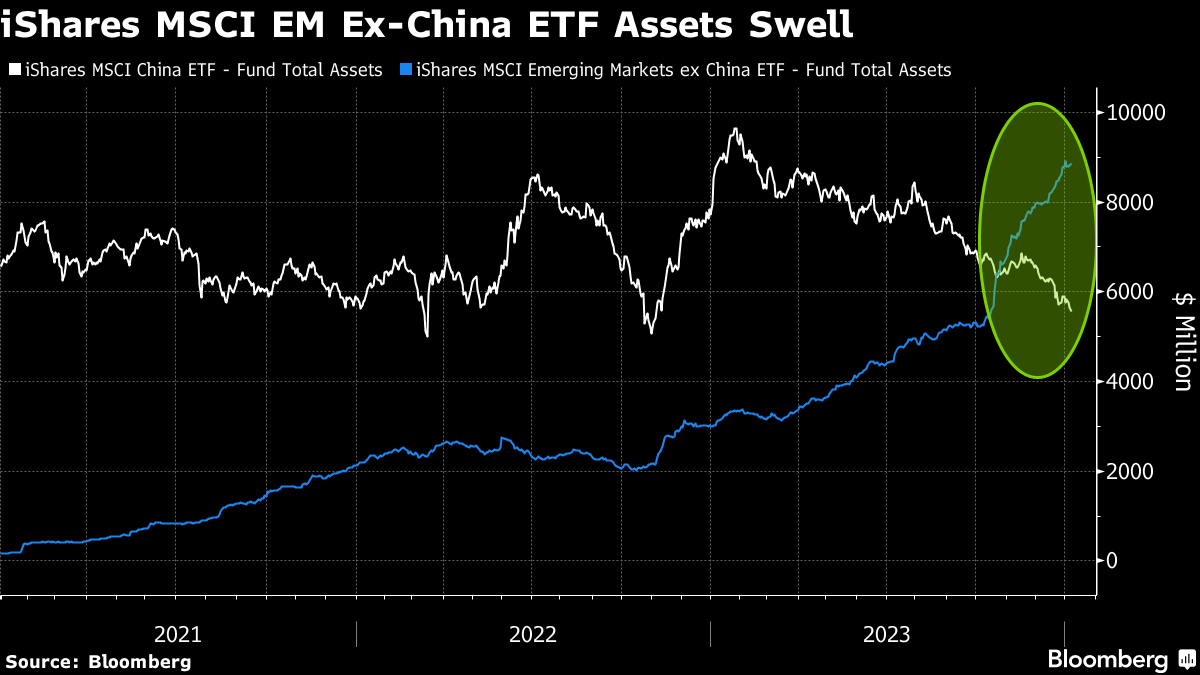
In a landmark shift, assets held by the iShares ETF for EM ex-China surged to about $8.8 billion from just $164 million at the end of 2020, exceeding that of a China ETF.
That's not to say the whole world has turned its back on China. Its $9 trillion market — the second-largest after the US — offers a trove of undiscovered firms that may deliver hefty gains. As HSBC Holdings PLC strategists noted earlier this month, there has been increasing interest from investors based in the Middle East, offsetting the outflows from the US.
Other Australian pension funds are taking a wait-and-see stance. AMP Investments, which currently has a slight underweight exposure, may change that in the coming years as China recovers, according to the fund's Chief Investment Officer Anna Shelley.
Yet the pivot away from China may accelerate as positive catalysts are missing at a time when the Federal Reserve shifts toward monetary easing, raising the odds of higher returns in emerging markets that are sensitive to the global economic cycle.
South Korea, Taiwan and India have so far seen a total inflow of more than $750 billion this year. Meantime, foreign investors have continued to sell China via stock connect links in the new year.
“Although much of the pessimism around China seem currently reflected in valuations, investors seem reluctant to step in,” said Romina Graiver, a portfolio specialist at William Blair International Ltd., one of the early entrants into EM ex-China strategies. “Over the past years China has become more difficult to navigate due to an unpredictable regulatory environment and government's prioritization of politics over economics in the wake of Covid.”
--With assistance from Rick Zhao and Irene Huang.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























